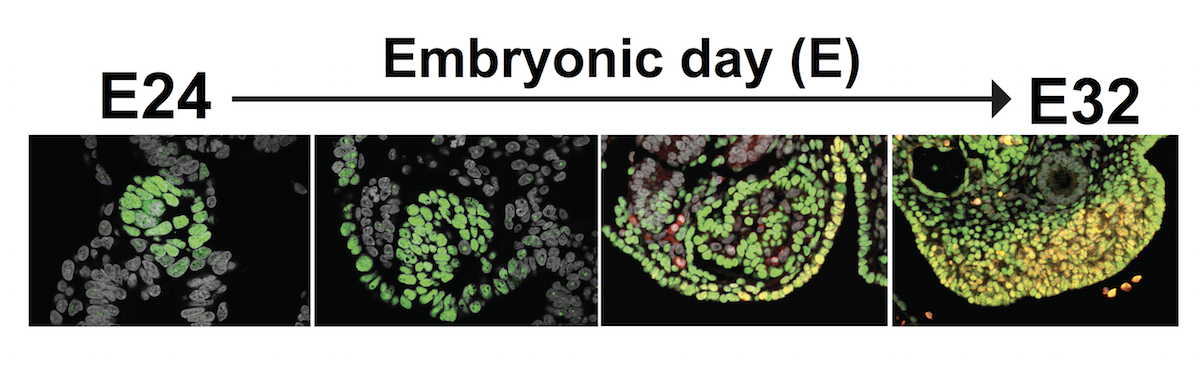
Early in human development, during the first trimester of gestation, a fetus may have XX or XY chromosomes that indicate its sex. Yet at this stage a mass of cells known as the bipotential gonad that ultimately develops into either ovaries or testes has yet to commit to its final destiny.
While researchers had studied the steps that go into the later stages of this process, little has been known about the precursors of the bipotential gonad. In a new study published in Cell Reports and co-led by Kotaro Sasaki of Penn’s School of Veterinary Medicine, an international team lays out the detailed development of this key facet of sexual determination in two mammalian models.
Photo credit: Kotaro Sasaki